| This page is owned by Gregjarlot. Please ask him before making relevant edits. |
|---|
| Austranland Empire | ||||||
| Reich Von Austranland (German) Impero di Austranland (Italian) Empire d'Austranland (French) | ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| Motto "Das Land der Berge, Das Land der Alpen" (German) "The Country of the Mountains, The Country of the Alps" | ||||||
| Anthem Nationalhymne des Reiches Austranland (German) | ||||||
| Capital | Vienna | |||||
| Largest city | Vienna | |||||
| Languages | German,Italian & French | |||||
| Official languages | German, French | |||||
| Recognised regional languages | Tyrolian, Morvandiaux | |||||
| Ethnic groups | Tyrolian, Burgonds, Savoy | |||||
| Demonym | Austrian Land | |||||
| Religion | Catholic | |||||
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional empire | |||||
| Emperor | ||||||
| - | 2001-Present | Charles Hasburg | ||||
| Chancelor of the Federal Council | ||||||
| - | 2001–Present | Sebastian Kurz | ||||
| Legislature | Federal Council | |||||
| - | Upper house | Council of Monteins | ||||
| - | Lower house | National Council | ||||
| History | ||||||
| - | Independence from France | 28th July 1998 | ||||
| - | Recognized | 20th April, 2001 | ||||
| - | 23 September 2017 | Official Country | ||||
| Area | 282,941 km² (109,244 sq mi) | |||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | 2016 estimate | 47 145 285 (32th) | ||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2016 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $955,982 billion | ||||
| - | Per capita | $879,997 | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2017 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $784,852 billion | ||||
| - | Per capita | $95,217 | ||||
| Gini (2012) | 59.2 medium • 17th | |||||
| HDI (2011) | high • 5th | |||||
| Currency | Schilling autrichien (AST) | |||||
| Time zone | Central Europe (UTC+1) | |||||
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy | |||||
| Drives on the | right | |||||
| Calling code | +1 245 | |||||
| ISO 3166 code | AST | |||||
| Internet TLD | AST | |||||
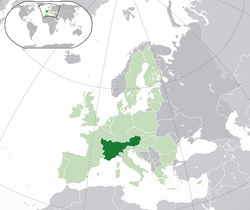
The Austranlandian Empire (phonotic: (/ˈɒstranlənd) (German: Reich Von Osternköland (phonotic: (/riːkh foʊn oʊstɛrnkolɪnd/) also called Austranland and ocasionally called the Austranland Empire, is an empire, composed of 18 landers and one capital territory in the Central Europe. It borders France, Germany, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Slovenia, Monaco and Italy.
The Austranland Empire was a part of Roman Empire in as early as 1st century and it was a sovereign state gthe next 1500 years. In 1998 along with other colonies of European Union, The Austranlandian Empire declared independence. France recognized their independence in April 20, 2001.
The economy of Austranland mostly depends on tourism. Austranland is the 7th most visited country by tourists in the world with 10.1 million international tourist arrivals. But the agriculture and industries have a great part of the economy of Austranland too.
Population of Austranland is 47 145 285, of which 1.2% are immigrants. Capital city of the country is Vienna, located in the lander of Vienna Land, in the Austrianland part. Over 1.867 million people live in the Vienna's metropolitan area.
Etymology[]
The German name for Austranland, Österreich, meant "eastern realm" in Old High German, and is cognate with the word Ostarrîchi, which first appeared in the "Ostarrîchi document" of 996. This word is probably a translation of Medieval Latin Marchia orientalis into a local (Bavarian) dialect. Austrianland was a prefecture of Bavaria created in 976. The word "Austria" is a Latinisation of the German name and was first recorded in the 12th century. At the time, the Danube basin of Austranland (Upper and Lower Austranland) was the easternmost extent of Bavaria, and in fact of all the Germans, as at the time the territory of the former East Germany was populated by Slavic Sorbs and Polabians.
Friedrich Heer, a 20th-century Austranlandian historian, stated in his book Der Kampf um die österreichische Identität (The Struggle Over Austrian Identity), that the Germanic form Ostarrîchi was not a translation of the Latin word, but both resulted from a much older term originating in the Celtic languages of ancient Austria: more than 2500 years ago, the major part of the actual country was called Norig by the Celtic population (Hallstatt culture); according to Heer, no- or nor- meant "east" or "easterns", whereas -rig is related to the modern German Reich, meaning "realm". Accordingly, Norig would essentially mean the same as Ostarrîchi and Österreich, thus Austria. The Celtic name was eventually Latinised to Noricum after the Romans conquered the area that encloses most of modern-day Austranland, around 15 BC. Noricum later became a Roman province in the mid-first century AD. Heer's hypothesis is not accepted by linguists.
History[]
Antiquity[]
Settled in ancient times, the Central European land that is now Austranland was occupied in pre-Roman times by various Celtic tribes. The Celtic kingdom of Noricum was later claimed by the Roman Empire and then made into a province. Present-day Petronell-Carnuntum in eastern Austria was an important army camp turned capital city in what became known as the Upper Pannonia province. Carnuntum was home for 50,000 people for nearly 400 years.
Middle Age[]
After the fall of the Roman Empire, the area was invaded by Bavarians, Slavs and Avars. Charlemagne, King of the Franks, conquered the area in AD 788, encouraged colonization, and introduced Christianity. As part of Eastern Francia, the core areas that now encompass Austranland were bequeathed to the house of Babenberg. The area was known as the marchia Orientalis and was given to Leopold of Babenberg in 976.
17th and 18th century[]

1800 in Dijon
During the long reign of Leopold I (1657–1705) and following the successful defence of Vienna in 1683 (under the command of the King of Poland, John III Sobieski), a series of campaigns resulted in bringing most of Hungary to Austrian control by the Treaty of Karlowitz in 1699. Emperor Charles VI relinquished many of the gains the empire made in the previous years, largely due to his apprehensions at the imminent extinction of the House of Habsburg. Charles was willing to offer concrete advantages in territory and authority in exchange for recognition of the Pragmatic Sanction that made his daughter Maria Theresa his heir. With the rise of Prussia, the Austrian–Prussian dualism began in Germany. Austria participated, together with Prussia and Russia, in the first and the third of the three Partitions of Poland (in 1772 and 1795).
19th century[]

The Empire of Austria was founded in 1804. Austria later became engaged in a war with Revolutionary France, at the beginning highly unsuccessfully, with successive defeats from Napoleon, meaning the end of the old Holy Roman Empire in 1806. In 1814, Austria was part of the Allied forces that invaded France and brought the Napoleonic Wars to an end.
It emerged from the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as one of the continent's four dominant powers and a recognised great power. The same year, the German Confederation (Deutscher Bund) was founded under the presidency of Austria. Because of unsolved social, political, and national conflicts, the German lands were shaken by the 1848 revolution aiming to create a unified Germany. The various different possibilities for a united Germany were: a Greater Germany, or a Greater Austria or just the German Confederation without Austria at all. As Austria was not willing to relinquish its German-speaking territories to what would become the German Empire of 1848, the crown of the newly formed empire was offered to the Prussian King Friedrich Wilhelm IV. In 1864, Austria and Prussia fought together against Denmark and secured the independence from Denmark of the duchies of Schleswig and Holstein. As they could not agree on how the two duchies should be administered, though, they fought the Austro-Prussian War in 1866. Defeated by Prussia in the Battle of Königgrätz, Austria had to leave the German Confederation and subsequently no longer took part in German politics.
The Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867, the Ausgleich, provided for a dual sovereignty, the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary, under Franz Joseph I. The Austrian-Hungarian rule of this diverse empire included various Slavic groups, including Croats, Czechs, Poles, Rusyns, Serbs, Slovaks, Slovenes, and Ukrainians, as well as large Italian and Romanian communities. As a result, ruling Austria–Hungary became increasingly difficult in an age of emerging nationalist movements, requiring considerable reliance on an expanded secret police. Yet, the government of Austria tried its best to be accommodating in some respects: The Reichsgesetzblatt, publishing the laws and ordinances of Cisleithania, was issued in eight languages; all national groups were entitled to schools in their own language and to the use of their mother tongue at state offices, for example. Many Austrians of all different social circles such as Georg Ritter von Schönerer and Karl Lueger promoted strong pan-Germanism in hope of reinforcing an ethnic German identity and the annexation of Austria to Germany. Despite the fact that it was Bismarck's policies that excluded Austria and the German Austrians from Germany, many Austrian pan-Germans idolized him, as well as wearing blue cornflowers, known to be the favourite flower of German Emperor William I, in their buttonholes, along with cockades in the German national colours (black, red, and yellow), despite the fact that they were both temporarily banned in Austrian schools, as a way to show discontent towards the multi-ethnic empire.

A lot of Austrian pan-German nationalists protested passionately against minister-president Kasimir Count Badeni's language decree of 1897, which made German and Czech co-official languages in Bohemia and required new government officials to be fluent in both languages. This meant in practice that the civil service would almost exclusively hire Czechs, because most middle-class Czechs spoke the German language, but not the other way around. The support of ultramontane Catholic politicians and clergy for this reform triggered the launch of the "Away from Rome" (German: Los-von-Rom) movement, which was initiated by supporters of Schönerer and called on "German" Christians to leave the Roman Catholic Church.
20th Century[]
Two world wars and an economic depression dominated the first half of the 20th century. World War I was fought between 1914 and 1918. It started when Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria was assassinated by the Yugoslav nationalist Gavrilo Princip. Most European nations were drawn into the war, which was fought between the Entente Powers (France, Belgium, Serbia, Portugal, Russia, the United Kingdom, and later Italy, Greece, Romania, and the United States) and the Central Powers (Austria-Hungary, Germany, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire). The war left more than 16 million civilians and military dead. Over 60 million European soldiers were mobilised from 1914 to 1918. Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire collapsed and broke up into separate nations, and many other nations had their borders redrawn. The Treaty of Versailles, which officially ended World War I in 1919, was harsh towards Germany, upon whom it placed full responsibility for the war and imposed heavy sanctions. The social revolutions sweeping through Russia also affected other European nations following The Great War: in 1919, with the Weimar Republic in Germany, and the First Austrian Republic; in 1922, with Mussolini's one party fascist government in the Kingdom of Italy, and in Ataturk's Turkish Republic, adopting the Western alphabet, and state secularism. Economic instability, caused in part by debts incurred in the First World War and 'loans' to Germany played havoc in Europe in the late 1920s and 1930s. This and the Wall Street Crash of 1929 brought about the worldwide Great Depression. Helped by the economic crisis, social instability and the threat of communism, fascist movements developed throughout Europe placing Adolf Hitler in power of what became Nazi Germany. In 1933, Hitler became the leader of Germany and began to work towards his goal of building Greater Germany. Germany re-expanded and took back the Saarland and Rhineland in 1935 and 1936. In 1938, Austria became a part of Germany following the Anschluss. Later that year, following the Munich Agreement signed by Germany, France, the United Kingdom and Italy, Germany annexed the Sudetenland, which was a part of Czechoslovakia inhabited by ethnic Germans, and in early 1939, the remainder of Czechoslovakia was split into the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia, controlled by Germany, and the Slovak Republic. At the time, Britain and France preferred a policy of appeasement.With tensions mounting between Germany and Poland over the future of Danzig, the Germans turned to the Soviets, and signed the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, which allowed the Soviets to invade the Baltic states and parts of Poland and Romania. Germany invaded Poland on 1 September 1939, prompting France and the United Kingdom to declare war on Germany on 3 September, opening the European Theatre of World War II.
The Soviet invasion of Poland started on 17 September and Poland fell soon thereafter. On 24 September, the Soviet Union attacked the Baltic countries and later, Finland. The British hoped to land at Narvik and send troops to aid Finland, but their primary objective in the landing was to encircle Germany and cut the Germans off from Scandinavian resources. Around the same time, Germany moved troops into Denmark. The Phony War continued.
In May 1940, Germany attacked France through the Low Countries. France capitulated in June 1940. By August Germany began a bombing offensive on Britain, but failed to convince the Britons to give up. In 1941, Germany invaded the Soviet Union in the Operation Barbarossa. On 7 December 1941 Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor drew the United States into the conflict as allies of the British Empire and other allied forces. After the staggering Battle of Stalingrad in 1943, the German offensive in the Soviet Union turned into a continual fallback. The Battle of Kursk, which involved the largest tank battle in history, was the last major German offensive on the Eastern Front. In June 1944, British and American forces invaded France in the D-Day landings, opening a new front against Germany. Berlin finally fell in 1945, ending World War II in Europe. The war was the largest and most destructive in human history, with 60 million dead across the world.] More than 40 million people in Europe had died as a result of World War II, including between 11 and 17 million people who perished during the Holocaust. The Soviet Union lost around 27 million people (mostly civilians) during the war, about half of all World War II casualties. By the end of World War II, Europe had more than 40 million refugees. Several post-war expulsions in Central and Eastern Europe displaced a total of about 20 million people.

World War I and especially World War II diminished the eminence of Western Europe in world affairs. After World War II the map of Europe was redrawn at the Yalta Conference and divided into two blocs, the Western countries and the communist Eastern bloc, separated by what was later called by Winston Churchill an "Iron Curtain". The United States and Western Europe established the NATO alliance and later the Soviet Union and Central Europe established the Warsaw Pact. The two new superpowers, the United States and the Soviet Union, became locked in a fifty-year-long Cold War, centered on nuclear proliferation. At the same time decolonisation, which had already started after World War I, gradually resulted in the independence of most of the European colonies in Asia and Africa. In the 1980s the reforms of Mikhail Gorbachev and the Solidarity movement in Poland accelerated the collapse of the Eastern bloc and the end of the Cold War. Germany was reunited, after the symbolic fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989, and the maps of Central and Eastern Europe were redrawn once more. European integration also grew after World War II. The Treaty of Rome in 1957 established the European Economic Community between six Western European states with the goal of a unified economic policy and common market. In 1967 the EEC, European Coal and Steel Community and Euratom formed the European Community, which in 1993 became the European Union. The EU established a parliament, court and central bank and introduced the euro as a unified currency. Between 2004 and 2013, more Central and Eastern European countries began joining, expanding the EU to its current size of 28 European countries, and once more making Europe a major economical and political centre of power. However, in June 2016 the people of the United Kingdom, in a national referendum on EU membership voted to leave the European Union.
Independence[]

Impact of Austranland independence
The 27 February 1985, the east of France would be recognized like an autonomous region or part of France, in Italy its same for the west regions. Three year ago, the part of France have much ambition, but the council of France refused.
The 16 January 1990, Austria, Liechtenstein and Switzerland officialized an idea to fusion these three territories. In Italy the west region have an autonomous statues. In France the revolt grew and the independence idea spread through Europe. Like in Catalonia.
The 24 November 1992, the french independentist have an idea, annexation with Italian autonomous, and with the idea of Austria Liecht. and Swiss union/annexation, and this idea is accepted with all part. So the countries are worried to an independendist feeling.
The 3 March 1993, all country concerned regroups in Prague, for a congress for this "crisis", and for know the future of their countries of Central Europe. And Austria, Liechtenstein and Switzerland create a referendum for know the future of these countries.
| Name | Vote |
|---|---|
| Ja! Oui! Yes! Sì! | 85 / 100 |
| Nein! Non! No! | 11 / 100 |
| ? don't Know | 4 / 100 |
The Referundum was the 20 April 1993. And was accepted, but the three countries wait Italian and French parts.
The name Austranland was found and accepted by the population the 18 Febuary 1994.
The 14 January 1996, Italy recognized the annexation by Austranland. But in France the revolt grow the parliament don't recognized the annexation and the idea of independence. The French Austranlandian organized a referendum in all french part. And only 20 vote on 500,000 voters have voted no so 499,980 have voted yes!,
The united nation, obligate France to recognized Austranland Empire. And the 28 July 1998, France recognized Austranland. And The 20th April 2001 Austranland was officially recognized to an official nations.
Geography[]
Austranland is situated in the Central Europe. Located in the Central Europe, Austranland has continental climate. Austranland has a rainy season which stretches from April into November. Mountains can cause wide variation in local wind speed and direction due to their sheltering and channeling effects adding to the climatic variation. In winter for mountains, have much snow for skiing. For litoral the sun is all time during the year. The highest mountain is the Mont Blanc with 4810m, Austranland have the totality of Alps Mountain.

Geography defines Central Europe's natural borders with the neighbouring regions to the North across the Baltic Sea namely the Northern Europe (or Scandinavia), and to the South across the Alps, the Appennine peninsula (or Italy), and the Balkan peninsula across the Soča-Krka-Sava-Danube line. The borders to Western Europe and Eastern Europe are geographically less defined and for this reason the cultural and historical boundaries migrate more easily West-East than South-North. The Rhine River which runs South-North through Western Germany is an exception. Southward, the Pannonian Plain is bounded by the rivers Sava and Danube - and their respective floodplains. The Pannonian Plain stretches over the following countries: Austria, Croatia, Hungary, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia and Slovenia, and touches borders of Bosnia and Herzegovina (Republika Srpska) and Ukraine ("peri- Pannonian states"). As southeastern division of the Eastern Alps,the Dinaric Alps extend for 650 kilometres along the coast of the Adriatic Sea (northwest-southeast), from the Julian Alps in the northwest down to the Šar-Korab massif, north-south. According to the Freie Universitaet Berlin, this mountain chain is classified as South Central European.

The highest river of Austranland is Rhône, rising in the Rhône Glacier in the Swiss Alps at the far eastern end of the Swiss canton of Valais, passing through Lake Geneva and running through southeastern France. At Arles, near its mouth on the Mediterranean Sea, the river divides into two branches, known as the Great Rhône (French: Le Grand Rhône) and the Little Rhône (Le Petit Rhône). The resulting delta constitutes the Camargue region. The sond is Po, the headwaters of the Po are a spring seeping from a stony hillside at Pian del Re, a flat place at the head of the Val Po under the northwest face of Monviso (in the Cottian Alps). The Po ends at a delta projecting into the Adriatic Sea near Venice. It has a drainage area of 74,000 km² in all, 70,000 in Italy, of which 41,000 is in montane environments and 29,000 on the plain. The Po is the longest river in Italy; at its widest point its width is 503 m (1650 ft).[1] The Po extends along the 45th parallel north. The river flows through many important Italian cities, including Turin (Torino), Piacenza and Ferrara.
Demographics[]
Largest Cities[]
This is a list of the country's largest cities by population
| Vienna Milan |
Rank | Name | State | Population |
Turin Marseille | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vienna | Vienna | 1,867,960 | ||||||
| 2 | Milan | Milanland | 1,368,590 | ||||||
| 3 | Turin | Piemont | 897,267 | ||||||
| 4 | Marseille | Provence | 858,120 | ||||||
| 5 | Genoa | Costa Azules | 549,733 | ||||||
| 6 | Zurich | Germanswish | 402,762 | ||||||
| 7 | Nice | Costa Azules | 343,895 | ||||||
| 8 | Graz | Südosternköland | 343,895 | ||||||
| 9 | Geneva | Romandia | 201,813 | ||||||
| 9 | Saint-Étienne | Lyonnais | 170,761 | ||||||
Vienna is the capital of Austranland because she have all of a politic capital city, the second highest city is Milan one of Fashion capital of the world. Turin is the Olympic city of 2006 Winter Olympic Games, after Marseilles the 4th highest city and host a part of Paris 2024 Summer Olympic Games, with Mermeide, after Genoa, Zurich a high economic city of Europe, Nice with the sun, Graz a cultural city. Geneva capital of United Nations, a very big place for much industries.
Département[]
54 Département are:
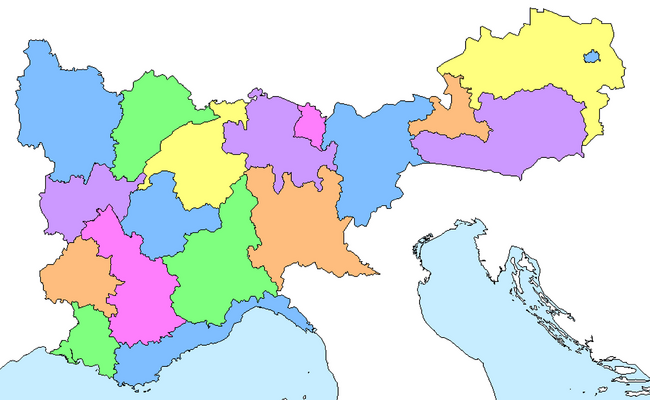
Lander[]
18 Lander for Austranland:
Politics[]
The Austranland Empire is a Federal parliamentary Empire unitary semi-presidential representative democratic republic with strong democratic traditions. The constitution of the Empire was approved by referendum on 20 April 2001 .It greatly strengthened the authority of the executive in relation to parliament. The executive branch itself has two leaders: the Emperor, currently Pierre, who is head of state and is elected directly by universal adult suffrage for a 5-year term, and the Government, led by the president-appointed Prime Minister.
Emperor & Chancelor[]
| 2ème Emperor of Austranland |
|---|
 Charles Hasburg None |
| 4th Chancelor of Austranland |
|---|
 Sebastian Kurz None |
The Emperor of Austranland (French: L'Empereur de l'Empire Austranien) is the executive head of state of Austranland in the Empire of Austranland. In French terms, the presidency is the supreme magistracy of the country.
The Chancelor of Austranland (French: Chancelier de l'Empire Austranien) is the executive head of state of Austranland in the Empire of Austranland. In French terms, the presidency is the government of Austranland.
The powers, functions and duties of prior presidential offices, and their relation with the Prime Minister and Cabinet, have over time differed with the various Austranian constitutions since 1967. The current President of Brion is Eduardo Leite, who succeeded Hugue Chapelle on 20 April 2018. During the 2019 Austran legislative election.
National Assembly[]
The Austran's parliament is a bicameral legislature comprising a National Assembly (Assemblée Nationale) and a Senate. The National Assembly deputies represent local constituencies and are directly elected for 5-year terms.The Assembly has the power to dismiss the government, and thus the majority in the Assembly determines the choice of government. Senators are chosen by an electoral college for 6-year terms (originally 9-year terms), and one half of the seats are submitted to election every 3 years starting in September 2008.The Senate's legislative powers are limited; in the event of disagreement between the two chambers, the National Assembly has the final say.The Government has a strong influence in shaping the agenda of Parliament.
Foreign relations[]
The Ministry of Foreign Relations, The Parliament and The President are responsible for Austran's foreign relations.
Law enforcement[]
Law enforcement in Austranland is provided by multiple police forces, five of which are national, Austran's agencies. The Police National Renforcer (National Police Corps) is the civil national police of Austranland. Along with patrolling, investigative and law enforcement duties, it patrols the national highway network, and oversees the security of railways, bridges and waterways. They also serve as the military police for the Brionian Armed Forces.
Military[]
The Austran's Army, Navy, Air Force and Armed Forces (National gendarmerie force) collectively form the Austran'sArmed Forces, under the command of the Supreme Defence Council, presided over by the Chancelor of Austranland. Since 1970, military service is voluntary.
The Austran's Army is the national ground defence force.
Culture[]
| Part of a series on the |
| Culture of Austranland |
|---|
 |
| History |
| People • Languages • Nationalism • Symbols • Religion |
| Topics |
| Architecture • Art • Cuisine • Music • Politics • Sports • Television • Transport |
| Portal |
Traveling permissions[]
Austranlandian can travel to almost every country without visas and citizens from almost every country can get in without visas. Austranlandian can get passports for free and Austranlandian passports grant visa free travel to 175 countries.

National TV[]
General[]
see also: ATV
TV Austranland, has borned the 01 January 2002. In first, January 2002, only the "Austrian" part have the channel on Television. The 01 July 2004, all lander have the chanel but no, Provence and Savoya, but the channel have a radio, 3
see also: Sport Kanal
The 13 January 2018, a new channel was created. A channel exclusively for Sports. After have confirm take part to the Mapperdonian International Basketball Federation.
Transport[]
Car[]
The Vehicle registration plate was invented the 25 November 2003. In first, in red, The emblems of Austranland and the denomination AT. In second In white a code the two first letter of the lander and two number and after two letter. In Blue, the flag of lander and the number of the department. In the bottom the city you are from and the postal code.
Planes[]

Logo of the companie
The national company of Austranland is Austranland Air, but the nickname is The3A, the company was formed the 06 March 2006. All aeroport National or regional in Austranland can host the plane of the company.
Languages[]
The officials languages of Austranland are French and German. But in real, French, German, and Italian are in majority speak by the population.
Economic[]

Geneva, Zurich, Lyon and Vienna are 4th great economic places in Europe, the industries are around Danube, Rhone and Po. The national money is Austranlandian Schiling AST. All have the monument famous in Austranland and a Famous People from Austranland. Like the History of the country.
Song[]
Mozart is the symbol of Austranland. Austranland's past as a European power and its cultural environment generated a broad contribution to various forms of art, most notably among them music. Austria was the birthplace of many famous composers such as Joseph Haydn, Michael Haydn, Franz Liszt, Franz Schubert, Anton Bruckner, Johann Strauss, Sr. and Johann Strauss, Jr. as well as members of the Second Viennese School such as Arnold Schoenberg, Anton Webern and Alban Berg. Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart was born in Salzburg, then an independent Church Principality of the Holy Roman Empire, which later became part of Austria, and much of Mozart's career was spent in Vienna.
Vienna was for a long time an important centre of musical innovation. 18th- and 19th-century composers were drawn to the city due to the patronage of the Habsburgs, and made Vienna the European capital of classical music. During the Baroque period, Slavic and Hungarian folk forms influenced Austrian music.
Sport[]
See detals: Sport in Austranland
The Austranland have many sport. Due to the mountainous terrain, alpine skiing is a prominent sport in Austranland and is extremely valuable in the promotion and economic growth of the country.Similar sports such as snowboarding or ski-jumping are also widely popular. Austrans athletes such as Annemarie Moser-Pröll, Franz Klammer, Hermann Maier, Toni Sailer, Benjamin Raich, Marlies Schild & Marcel Hirscher are widely regarded as some of the greatest alpine skiers of all time, Armin Kogler, Andreas Felder, Ernst Vettori, Andreas Goldberger, Andreas Widhölzl, Thomas Morgenstern & Gregor Schlierenzauer as some of the greatest ski jumpers of all time. Bobsleigh, luge, and skeleton are also popular events with a permanent track located in Igls, which hosted bobsleigh and luge competitions for the 1964 and 1976 Winter Olympics held in Innsbruck. The first Winter Youth Olympics in 2012 were held in Innsbruck as well.
Football[]
2019 MIFF World Cup Austranland will competed at this big tournament.
Handball[]
Austranland have win the Monthly Cup January 2019. And have win the tournament in front of Brandenburg. It is held in Brandenburg during the events of March 2019And Austranland have host the Monthly Cup February 2019. And the second win Monthly Cup February with Rhinea for host the Monthly Cup April 2019.
Austranland will competed at the 2019 MIHU World Men's Handball Championship.
Mapperdonian Games[]
See National Committee Austranland
Austranland have participate at the first 2018 Mapperdonian Winter Olympic Games. And have annonced the 31 January 2017 would host the 2018 Mapperdonian Summer Olympic Games . And have Presented a bids for Lyon: Lyon bid for the 2018 Summer Olympics .
See details: Austranland at 2019 Mapperdonian Winter Sports Championships[]
In Febuary-March 2019 Austranland compete at 2019 Mapperdonian Winter Sports Championships in Munich, Rhinea, a total of 15 sports Austranland play, the show was watched by 10 Million Austrans and be a great party in all the country. Insee National Institute of Statistic of the country have see the growth of the national spirit of Austranland! Now the country is not only a new country but now a great and proud nations! Austranland is the winning country of the 2019 Mapperdonian Winter Sports Championships
See Details: Milan bid for the 2019 Mapperdonian Sports Championships[]
After this wonderful experience in the new contest Mapperdonian Sports Championships, Austrans will host the 2019 Mapperdonian Sports Championships in Milan.
See details: Innsbruck bid for the 2020 Winter Sports Championships[]
After this wonderful experience in the new contest Mapperdonian Sports Championships, Austrans will host the 2019 Mapperdonian Sports Championships in Milan.
Superbowl[]
Austranland have created the 7 Febuary 2018 the Mapperdonian Super Bowl. Austranland have host the first edition in the city of Milan during the 20 Febuary 2018 to the TBA 2018.
Holidays[]

|
Date |
Holidays |
Porcent |
|---|---|---|
| 1st January | New Year's Day | A day to celebrate the first day of the year on the Georgian Calendar. |
| Easter Sunday | Easter Sunday | A day to celebrate the day Jesus rose back from the dead. |
| 20 April | Independence Day | A day to celebrate the independance of Austranland |
| 19 May | The Peace Day | A day to celebrate peace & love in all Austranland. |
| 11 November | War Day | A day for Remember all the war. |
| 24 December | Christmas Eve | The day before Christmas |
| 25 December | Christmas | Christmas |
| 31 December | New Year's Eve | The day before New Year's Day. |
Allies[]
See Details: Austranland–Rhinea relations Austranland is the Foundator of Community of Democratic Nations since the 4 October 2017
Autranland Allies:
 Alboran: allies the 01 October 2017.
Alboran: allies the 01 October 2017.Western Republic: allies the 01 October 2017.
 Slavonica: allies the 02 October 2017.
Slavonica: allies the 02 October 2017.Francoisa: allies the 25 November 2017.
 Archeldwav Republic: allies the 13 December 2017.
Archeldwav Republic: allies the 13 December 2017. Fyorr: allies the 15 December 2017.
Fyorr: allies the 15 December 2017. Alatia: allies the 02 Febuary 2018.
Alatia: allies the 02 Febuary 2018. Novasrbija: allies the 13 Febuary 2018.
Novasrbija: allies the 13 Febuary 2018. Lestuvia: allies the 29 July 2018
Lestuvia: allies the 29 July 2018 Athis: allies the 9 March 2019
Athis: allies the 9 March 2019 Rhinea: allies the 9 March
Rhinea: allies the 9 March ABSA Germany: allies the 1 June 2019
ABSA Germany: allies the 1 June 2019 Duchy of Hamburg: allies the 21 June 2019
Duchy of Hamburg: allies the 21 June 2019
Austranland have develloped his national realtion since 2017, All country have a good relation with Austranland, and Austranland to.